What is eLearning? Everything you need to know about it

Have you ever heard about e-learning? For many people, it’s the tool of the moment in the new digital world. It not only came to facilitate the learning process, but also to offer a new way of developing skills in work environments. According to different sources, it is estimated that 90% of organizations in the United States offer their employees some form of digital learning. This speaks of how the training landscape has changed in the last few years and what can we expect in the immediate future.
What is eLearning?
eLearning is any type of learning that uses digital technology to deliver lessons without an in-person component. eLearning can be delivered to learners using any digital medium. They may access a course using their desktop computer or laptop, download an elearning app onto their phone, or even stream a recorded session on an internet-connected television.
Examples of eLearning include: on-demand courses, learning apps, and webinars. This type of learning can also encompass less formal types of digital educational content like podcasts, blogs or eBooks developed for the purposes of instruction.
In short, the purpose behind content development is more important than the medium. While content created for eLearning can be entertaining, its primary purpose is to instruct. Creating such content requires either a multi-talented individual, or more commonly, a team of learning professionals.
The Advantages of eLearning
eLearning is valuable because it expands access to learning opportunities. Students and instructors don’t need to be in the same room, or even the same country. An aspiring pastry chef in Idaho can take a class from a Michelin star chef in France without buying a plane ticket.
In corporate settings, eLearning allows for consistent training across locations without the cost of sending a trainer to each location. Asynchronous eLearning also delivers the same training to people on different shifts or in different timezones without having to align multiple schedules.
In both corporate and educational settings, eLearning allows students to access learning opportunities at the times and locations that work best for them. Sometimes that will mean logging in to a synchronous webinar, and other times it might mean completing a lesson on a language learning app while riding the subway to work.
Types of eLearning
eLearning can be delivered in a variety of forms to meet learner needs and instructional goals. Broadly, learning opportunities may be divided into synchronous or asynchronous or elearning.
Synchronous learning is delivered at a specific time, with students and the instructor all engaging at the same time. An interactive webinar is an example of synchronous eLearning. Asynchronous learning is delivered on-demand. The student can interact with the content on their schedule. Watching a recording of that same webinar because you were in meetings during the original presentation would be asynchronous learning.
The following types of eLearning may be delivered either synchronously or asynchronously.
- Social learning – Social learning is the act of learning by interacting with colleagues or classmates. Discussion questions, message boards, and the social networking features built into some learning management systems (LMS), encourage students to learn by engaging with each other.
- Microlearning – This style of eLearning breaks topics into small chunks, allowing students to complete a session in as little as a minute. The reasons for microlearning are two-fold. First, learners don’t always have time for longer lessons and may be able to more easily fit microlearning into their schedule. For example, a two-minute video emailed to an employee with a couple of questions for assessment, could be easier to fit into the day of an hourly worker. Second, microlearning allows learners to engage with smaller volumes of material more often, which can aid memory retention.
- Adaptive learning – A skilled instructor tracks a student’s progress and adjusts their lessons accordingly. Adaptive learning tries to emulate that behavior using preset rules or algorithms. For example, if a student struggles with certain questions on a quiz, the algorithm might serve more content on the topics related to those questions.
eLearning can also be used in conjunction with other delivery styles to create blended learning opportunities. Blended learning combines eLearning with face-to-face instruction. A classroom teacher who asks students to watch an instructional video and take an online quiz before the next class session is employing blended learning.
When designing eLearning lessons and modules, instructional designers and eLearning developers create for a specific technology platform. This could be a web-based learning management system, a mobile phone, or even a virtual reality headset. Since each of these platforms has different capabilities each one offers a slightly different learning experience.
eLearning Job Roles
eLearning is a broad field with many different kinds of opportunities for the right candidates. Delivering quality eLearning experience most often requires a team. Sometimes a multi-talented individual can fill the need, but the complexity of the work makes this a difficult strategy to maintain. Here are some common eLearning job roles
- Instructional designer – Plans and oversees creation of the learning experience, making decisions about content, activities, and assessments.
- eLearning developer – Uses eLearning software to create interactive learning modules. This role may overlap with that of the instructional designer.
- Learning management system administrator – A technical expert in the learning management system (LMS) used by an organization. They may load the content, enroll users, and offer user and facilitator support.
- Project manager – Manage the full life-cycle of an eLearning project including design, development and delivery.
- Writers – A broad category that can encompass several specialities including curriculum writing, script writing, and assessment or item writing.
- Multimedia and graphic designers – These professionals specialize in design, videography, or other audio-visual aspects of learning production.
These are just a few of the most common eLearning jobs available. If you’re hiring for eLearning roles, these are a good starting point for deciding what types of professionals you may need.
Skills required for a career in eLearning
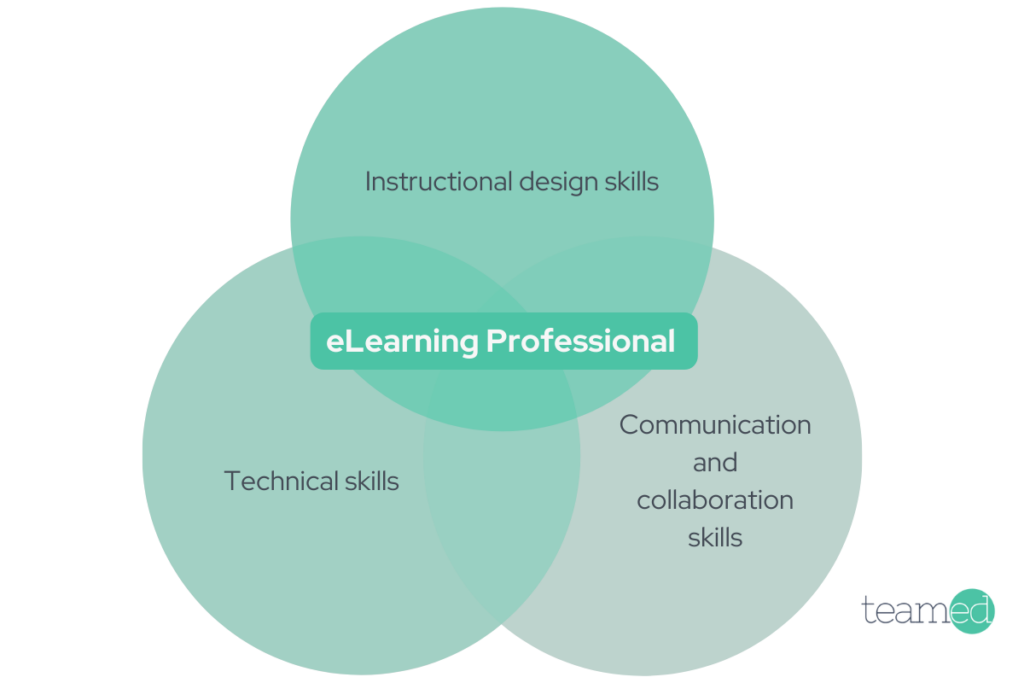
eLearning professionals bring a wide range of skills. While skill demands vary across roles and specialities, three stand out as essential for anyone working in eLearning.
- Instructional design skills – not just for instructional designers. Everyone who works in eLearning should have a basic understanding of instructional design principles.
- Technical skills – Since eLearning is delivered by technology, technical skills are an essential part of the role. This includes at least a basic understanding of learning management systems and often includes eLearning software, basic coding and troubleshooting.
- Communication and collaboration skills – Anyone who works on a team needs communication and collaboration skills. eLearning professionals are no exception.
These skills form a strong foundation for anyone seeking a role in eLearning, but they’re just a starting point. Skilled eLearning professionals build a range of skills to fit different specialties and project demands.
Training and education options for eLearning jobs
Whether you’re looking to expand your eLearning skills or wondering what to look for when hiring an eLearning professional, there are many training and education paths to consider. Most eLearning professionals do have at least a Bachelor’s degree. Some choose to pursue Master’s or post-graduate certification programs to help hone their skills in a specific area. There’s even an authorized trade school, IDOL Courses Academy, that offers a certificate in instructional design.
Outside of these more traditional academic settings, you can find some reputable programs offering training for eLearning professionals. Here are a few that fall into that category:
- Teacher Transition – A course to help transitioning teachers become curriculum and instructional designers
- Mastering Instructional Design – Live and on-demand classes as well as workshops from an experienced instructional designer
- Instructional Design Principles for Course Creation – A bootcamp from Eduflow Academy that teaches online course design
- Instructional Design Institute with Luke Hobson – A community offering professional development for instructional designers
While education and certifications are certainly part of the equation, hands-on experience counts too. Many eLearning professionals bring a wealth of knowledge from internships, contract jobs, and prior work.
Basics of eLearning Design and Development
eLearning design and development is the process used to create learning modules and other digital learning opportunities. Successful eLearning design and development requires four basic parts: instructional design, a learning management system, content, and assessments and evaluations.
Here’s a closer look at each of these elements of eLearning design and development:
Part 1: Instructional Design
Instructional design is the process of planning and overseeing the creation of the learning experience. Instructional designers can use several models to help them do this effectively.
- ADDIE model – Stands for the five phases of instructional design: analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation.
- SAM model – Stands for Successive Approximation model, which is a simplified version of ADDIE. It begins with preparation then moves into an interactive design phase followed by an iterative development phase.
- Agile methodology for rapid development – A software development model often used in instructional design to manage a project through collaboration and iteration.
An instructional designer may use one of these models or a combination of them. Please note there are additional models available. A skilled instructional designer should be able to explain the pros and cons of different models and why they chose the ones they did.
Part 2: Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning management systems are used to manage, deliver, and track employee training or student learning. Common LMS used in education include Canvas, D2L, Blackboard and Moodle. Corporate training programs may use these as well, or choose from any of the wide range of learning management systems designed for businesses such as Cornerstone on Demand, Docebo, Absorb, etc.
Some eLearning professionals have expertise in a specific LMS others bring more general knowledge. Only the LMS Administrator truly needs to be a technical expert in the specific LMS being utilized. For the most part, other professionals can get up to speed by reviewing the basic functions available in a specific system.
Part 3: eLearning Content
Content development for eLearning starts with learning objectives. These are statements that describe what learners are expected to be able to do or know at the end of the lesson. Learning objectives are often drafted using Bloom’s Taxonomy, a framework that classifies learning objectives by level of complexity.
Because eLearning is delivered digitally, it is easy to integrate multimedia into the modules. This could include videos, audio recordings, images, or interactive elements.
Learning modules and mobile learning apps often use gamification, a type of strategy that helps to motivate students by using elements commonly found in games. These might include badges, leader boards, or a points system. If a classroom teacher ever helped you study for a test by having the class play a trivia game, you’ve seen gamification at work.
Part 4: Assessments and evaluations
A complete learning module or course includes assessments and evaluations to gauge the learner’s level of knowledge. Designing quality assessments and evaluations takes skill. Just asking a few multiple-choice questions may not fully reveal a learner’s progress.
Instructional designers who work in the corporate learning space, often use the Kirkpatrick Model of Evaluation and may even have a psychometrician on staff to support in collecting and evaluating data. In the education space, item writers and assessment writers are in strong demand.
eLearning Best Practices
During the development of modules and learning content, teams are guided by eLearning Best Practices. These practices make lessons more effective and accessible.
In fact, accessibility and inclusivity are core tenets of eLearning. eLearning professionals use the Universal Design for Learning framework to support accessibility and inclusion. UDL encourages design that engages learners, presents information in multiple ways, and provides various opportunities for learners to express what they’ve learned.
Personalization is an eLearning best practice that is made possible by technology. Machine learning and AI can help to personalize the learning experience. Truly personalized learning allows the learner to set the pace and even select which lessons they will engage with at any given time.
Although students aren’t necessarily learning at the same time or in the same place, well-designed eLearning creates opportunities for social learning. These might include discussion boards, social media groups, or video conferencing sessions.
eLearning Technologies
Of course, technology is an essential element of eLearning. Professionals in eLearning use a range of technology to author, deliver, and monitor learning experiences. Commonly used authoring tools include:
- Articulate Storyline
- Articulate Rise
- Adobe Captivate
- Lectora
Throughout the design and development process, eLearning professionals build for a specific delivery method. Modules may be delivered via desktop or laptop computer, on mobile phones, or via virtual or augmented reality. Each of these delivery methods shapes the content and the learner’s experience. Here’s a closer look at some of these delivery technologies.
Mobile learning
Sometimes called mLearning, mobile learning has become especially important because more than 60% of the population of the world uses a mobile device to access the internet. Making learning mobile accessible means more people can access learning in more places.
Many learning providers use apps to deliver learning opportunities in mobile formats. Popular mobile learning apps include Duolingo for language learning, Google Learning which connects students and teachers, and Khan Academy which teaches common classroom topics to students of all ages.
Professional learning and continuing education can also be delivered via mobile learning. Popular learning management systems have mobile apps, including Docebo, TalentLMS, and Adobe Learning Manager.
Many eLearning platforms include responsive players that detect the type of device being used and adjust the layout accordingly. Mobile-responsive learning allows a learner to access training across desktop, tablet, and mobile devices.
Mobile devices are ideal delivery systems for micro-learning, short modules or quick learning activities delivered when and where the learner needs them. Many employers have embraced microlearning for employee training and onboarding because it’s affordable, flexible, and faster to delivery.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Alongside these delivery methods, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can be used to customize learning experiences and improve modules over time. These technologies can be used to create personalized learning paths and adaptive learning. AI can even help answer student questions when an instructor is not available.
Advances in AI technology are driving its wider adoption in elearning. Although AI can speed up course creation and help support students, it is only a tool. It cannot yet, and more importantly, should not, replace real people who bring human wisdom, compassion, and awareness to the development of training materials.
AI is particularly powerful when paired with data. Education and training providers can use AI to analyze student success metrics, monitor student engagement, and recognize patterns in learner feedback. All of this information can be used to improve the learning experience.
Machine learning is a useful tool for personalization and customization. When eLearning tools are equipped with eLearning, they can adjust to the needs of individual students. This could include something as simple as repeating questions on concepts the student has struggled with in the past, or as complex as creating a guided instructional experience for each learner.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is an up-and-coming technology that can be especially valuable for immersing students into an experience. It has been used in the automotive, manufacturing, medicine and defense industries to allow employees to learn without putting health and safety at risk. Creating eLearning modules in VR often requires the help of animators.
Augmented Reality (AR) is similar to VR, in that it can offer students earlier access to experiences without risking safety or property. It overlays information or graphics on real life objects or settings. Welding is one industry that has embraced AR training as a safer alternative.
eLearning Industry Trends
The eLearning market has grown rapidly over the last decade. In 2020, that growth received an extra bump when lockdown measures made eLearning the preferred option. Many new students and providers entered the market. The repeal of lockdown orders caused little change in the overall eLearning market.
The global market for eLearning was valued at $214.26 Billion USD in 2021. By 2030, that valuation should surpass $1 Trillion. Those numbers don’t even include businesses providing training to their own employees.
Another way to understand projected growth is by tracking investments. Between 2017 and 2021, there was a 6x increase in venture-capital funding for education in the U.S. alone. That looks like smart money when you consider that the number of people using online learning platforms has grown from 650.8 million in 2021 to 733.30 million in 2023. That doesn’t include online university education or professional certificates which have seen a much smaller increase.
As the market becomes more saturated, both learners and businesses have become more focused on data analytics. Gathering learner insights helps both eLearning teams and the organizations that fund course development. eLearning teams use data to iterate and improve their offerings, while organizations use data to assess their return on investment. Many organizations even have data analysts or learning scientists who specialize in gathering and understanding learner data.
Now Is a Great Time to Hire or Apply for eLearning Jobs
In summary, eLearning is a growing field with many and varied opportunities for learning professionals. The majority of eLearning professionals work on teams to create learning opportunities for everyone from K-12 students to corporate employees to self-directed learners. Although eLearning is technology enabled, it’s still student-focused. All of the technology and design elements combine to provide responsive, personalized, and accessible learning opportunities.
eLearning recently experienced a surge in popularity, and the industry is expected to keep growing. More employers are looking for ways to use eLearning with their teams and schools and colleges are offering more online learning opportunities for students.
If you’re looking for a job in eLearning, visit our Teamed Job Board. For those on the hiring side of the equation, we offer a full range of flexible hiring support. Whether you want to list a job, connected with expertly vetted professionals, or have us handle the hiring process, we’re here to help. Contact our hiring experts today to get started.